A Look Back Into The History of Search Engines
Have you ever stopped to wonder about life without search engines: our friendly assistants that hang out on our smartphones, tablets, and computers, ready to answer our every question? This wasn’t always the case. In the past, searching meant trawling through volumes of encyclopedias or paying a visit to the library. Oh, how far we’ve come! This blog post will unravel the fascinating history of search engines from the absence of search engines to the current complex landscape. Explore more about SEO. Click here!
Table of Contents

Exploring The Origin And History Of Search Engines From 1900s To 2023
In the dawn of digital time, individuals’ quests for knowledge were not quickly resolved with a simple Google search. Back then, the thirst for information had to be satisfied strictly through human interaction and resources like libraries and classrooms. Long gone are those days, all thanks to a series of exponential advancements that would forever change the face of information retrieval – the birth of search engines.
The Late 1990s: Beginning Of Search Engine Invention
As the internet grew in prominence in the late 20th century, there was a parallel expansion taking place in recognition of the need for smarter ways to wade through virtual mountains of information available.
1992: Invention Of Archie
Archie, short for “archive,” heralded a new era of information retrieval. No longer did people need to know the precise location of a document out of millions on the burgeoning internet. Instead, Archie crawled these untamed digital territories, compiling a rudimentary database of filenames for reference, a game-changer in those times indeed!
1993: Jonathan Fletcher Launched JumpStation
Records were set, and records were smashed. Jonathan Fletcher stepped into the ring in 1993, introducing JumpStation, the first-ever web search engine that utilized a web robot to crawl and index pages, thus amplifying the command of the information at our fingertips.
1994: WebCrawler And Lycos Introduced

The stage was set for an explosion of new players as the importance of search engines became more apparent. At the helm in 1994, two pioneer search engines appeared on the fountainhead of web searching. WebCrawler laid the groundwork as the first complete search engine that indexed entire web pages, including their text content. Simultaneously, the internet behemoth Lycos made its appearance, boasting a significantly more comprehensive directory of sites for users to search through.
1995: The Emergence Of AltaVista
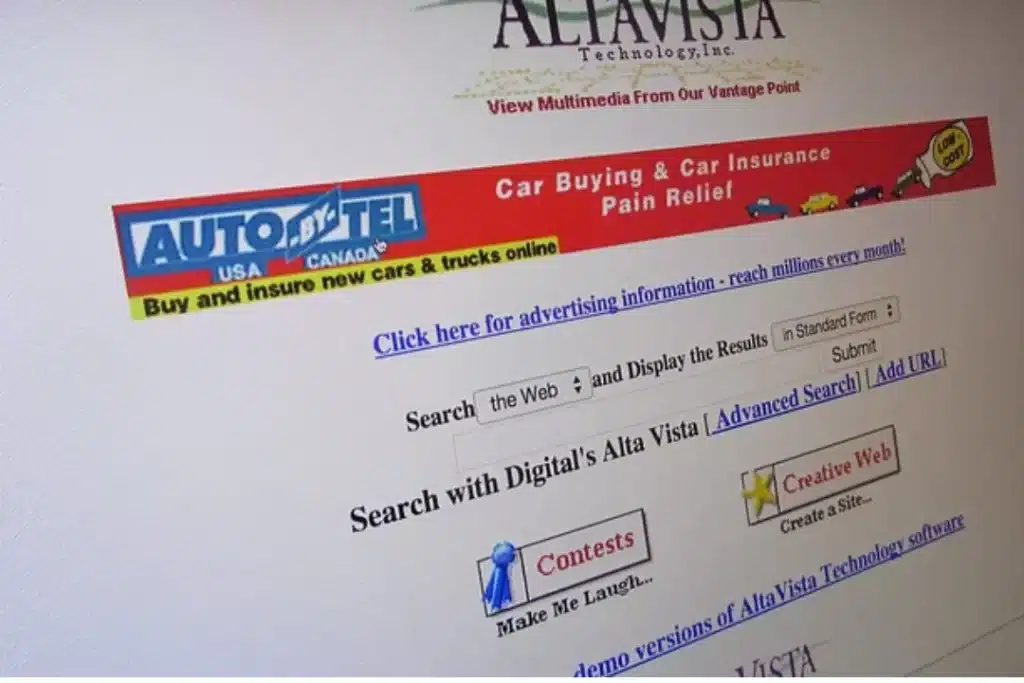
Shifting into the era better known as the ‘First Search Engine War’, came Digital Equipment Corporation’s AltaVista. Indexing a grand total of around 20 million webpages, AltaVista was the first to perfect a multi-threaded crawler (Scooter) that could cover many more webpages that had been available up till the dawn of this extraordinary information-finding giant.
1996: The Dawn Of Meta Search Engines
Metasearch engines shone their torches into cyberspace for the first time, thereby laying a milestone in detecting information across the digital frontier. These fastidious workers’ brilliant algorithms allowed them to simultaneously employ multiple search engines and yield pertinent results from each of these engaged search engines, earning them that much-needed edge over opponents.
1997: Google's Emergence And The Rise Of Specialized Engines
Google entered the scene in 1997 and it was a game changer. Stanford University students Larry Page and Sergey Brin created a superior, user-friendly algorithm that grabbed web users’ attention. Google became an ally of speed, empowering users to access results in milliseconds. This new search engine also sparked the inception of specialized search engines, focusing on niche information like recipes, work, or movie rating searches.
1998: Relevance And Real-Time Search
With the existence of an ocean of information, the great challenge of making things relevant was top of mind. Tools like DirectHit began to focus on the notion of “popularity” as a ranking factor, allowing people to access popular and trending information in real-time.
1999: The Directory Dream And Mobile Search
As the web continued to burgeon, companies began to grapple with its organization. A number of innovative search entrepreneurs sought to address this issue, launching sites dedicated to sorting and classifying various web pages. Simultaneously, web searches became an intrinsic part of mobile devices, introducing a whole new era of convenience and revolutionizing on-the-go search behavior.
2000: Image And Multimedia Search
Ever tried to describe a visual element using just words? The year 2000 ushered in the era of image and multimedia search – an upgrade that considerably enhanced the user search experience. Forget about slogging through oceans of text information, the dawn of image and multimedia search turned visual forms of information into searchable commodities.
2001: Microsoft Launched MSN Search
Remember the day when we couldn’t “Google” things? Yes, that’s because prior to 2001, MSN was one of the leading search engines! Launched by Microsoft, MSN Search prided itself on its proprietary web crawler and technology that delivered relevant hits to users during the embryonic days of the digital age.
2002: Concept Of MetaSearch Introduced
The year 2002 brought about a revolution in the world of search with the introduction of metasearch. Unifying the results from various search engines, metasearch offered an eagle-eye view, aggregating the vast expanse of information into a streamlined and relevant list.
2003: Google Launched Google AdSense
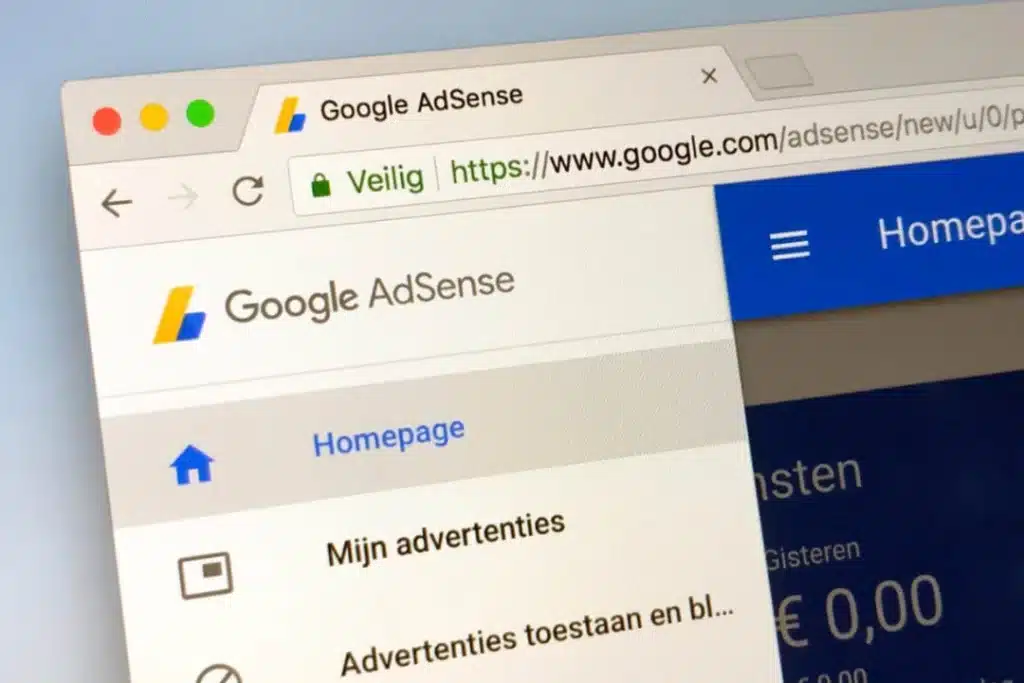
In an audacious move to capitalize on the growing internet landscape, Google expanded its influence by launching Google AdSense in 2003. Making Digital Advertisement a profitable venture, AdSense revolutionized the web business model by enabling website owners to serve targeted ads to their users, thereby creating an additional income stream from their online traffic.
2004: Google Images Launched
Ever needed an image for your PowerPoint presentation, blog post, or research project and wondered where to find it? Fortunately, Google Images has your back. Launched in 2004, this specialized search service changed the way we search and view images on the internet, enriching our visual experiences.
2005: Google And The Dawn Of Personalization
Remember the thrill when Google started tailoring search results according to personal search history and location data? Yes, 2005 was the year of this major foray into personalized search. By integrating sophisticated algorithms and artificial intelligence, it allowed Google to curate search results that reflected user’s needs at a personal level, thereby transforming the search game entirely.
2006: The Advent Of Universal Search
As technology evolved, so did the means for procuring information. Marking its pioneering efforts, Google’s Universal Search burst forth in 2006, seamlessly blending videos, images, and news stories directly within search results. It introduced a holistic search approach, widening the parameters of finding and representing information.
2007: The Rise Of Mobile Search

In 2007, Apple Inc. magnificently presented the world with the iPhone: a pocket-sized supercomputers with capabilities that transcended nation boundaries. Enter the mobile search revolution. Google, clasping the potentially drastic changes these handheld convenience-bringers impose on consumer behavior, began to accommodate mobile queries, altering the internet’s course towards a mobile-first direction.
2008: The Emergence Of Search Suggest And Real-Time Results
In terms of software innovation, 2008 proved to be pivotal. Search Suggest (or autocomplete) came to the forefront as Google endeavored to assist users by recommending search queries in real time, even before they finished typing them. Google further launched groundbreaking updates focusing on speed and efficiency, bestowing internet users with near-instantaneous search results.
2009: Bing And The Reign Of Rivalry
In a world that had come to rely heavily upon the dynamic landscape of researching and retrieving information online, another significant playmaker entered the battlefield: Bing. Launched by Microsoft, Bing came with the optimistic promise of advancing more accurate results based on a user’s natural, everyday language, ruffling up a unique rivalry in the search engine kingdom that exists to date.
2010: Personalized Search Evolves
Throughout 2010, search engine capabilities were further expanded, now tailored to match an individual’s past searches and web-browsing history, creating an unprecedented level of personalization. This evolution helped single searches become some of the most impactful strokes on one’s keyboard, supercharging the users’ experience across the immense digital cosmos.
2011: Google Introduced Google Instant
In 2011, Google took technical amelioration by storm again when it unveiled “Google Instant”. Its prowess to load search results instantaneously, as one typed, redefined speed and precision in the panorama of online exploration. Formulated under the slogan, “search before you type”, this benchmark unveiling formed their innovative status, transgressing the spheres of digital research and retrieval.
2012: DuckDuckGo Emerged As A Search Engine, Google's Penguin Update
The year 2012 welcomed the birth of DuckDuckGo, a new player in the search engine game, breaking the dynastic hold of Google with a fresh and unique perspective on the integrity of user privacy.
In the same year, Google rolled out the landmark “Penguin Update.” This significant algorithmic change was designed to down-rank sites with manipulative links, penalizing tactics against Google guidelines, and rewarding high-quality websites, thus transforming the future landscape of SEO.
2013: Google's Hummingbird Update
Imagine asking your search engine a question and getting direct and useful answers instead of just blue links. That’s the power Google’s Hummingbird introduced in 2013. It brought about a transformative change by factoring in semantic contextual matching in the search. This innovative update pivoted Google to a focus on understanding user queries and intentions to deliver more refined and informed responses.
2015: Google's Mobilegeddon Update
The dramatic prolificacy of mobile browsing essentially birthed the ‘ Mobilegeddon’, Google’s yet another instrumental update unleashed in 2015. This compelled websites to be mobile-friendly, adjusting the ranking of sites narrowed down to their mobile-compatibilities. Driven by this, the web frontier became a much more digitally inclusive and accessible framework than ever before.
2016: Google Introduced RankBrain Algorithm

2016 introduced us to RankBrain – a machine learning artificial intelligence rolled out by Google. Its primary function was to precisely interpret search queries just like humans do and provide the appropriate search results. It procrastinated semantic searching to the next level, innovating the search framework, and ensuring optimization strategies transitioned to more conversational content and user focus responses.
2017: Google Introduced Featured Snippets
Visualize an internet world where you’d perform a search and instantly get the information you need right on the search result page – exact and brief. Magic of 2017’s Google Featured Snippets fulfilled this need, selectively highlighting portions of the website’s content that directly answered search queries.
2018 Google Introduced Mobile-First Indexing
In 2018, Google revolutionized the way search engines interacted with mobile sites by rolling out its Mobile-First Indexing update. Now, the mobile version of a website is considered the ‘’primary’’ version for indexing and ranking, thus necessitating businesses to master mobile user experience to ensure their endurance and winsomeness on the digital forefront.
2019: Google Introduced BERT
Around the corner of 2019 Google’s Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers, better known as BERT, bringing it on record as the most significant update so far. BERT honed the search engine’s ability to grasp the organic, conversational language, and gauge both order and context in queries to cater to fine-tuned and improved accurate ranking.
2020: The Covid-19 Era
Life as we knew it was suddenly put on pause when COVID-19 hit the world. With people compelled to work and learn from home, search engines found invigorating roles, becoming primary channels for news, health information, remote work and education sources, and even entertainment. The pandemic stipulated an online search behavioral shift that forcefully moved the world closer to real-time information retrieval at a scale fundraise before this period.
2021: Google Introduced MUM
The Search Cavern of 2021 took a giant leap beyond traditional linchpins! Unleashing the Multitask Unified Model (MUM), Google aimed to decipher and process not just phrases, but sentences, and given large documents. With its capabilities of extracting intricate levels of semantic meaning from comprehensive text, this update held promises of re-engineering searching.
2022: OpenAI GPT-4 Integration
Ever since the introduction of AI-generated writing through OpenAI’s GPT-3 model, the digital world buzzed for what’s coming next – A technology that understands text context in a whole new depth and accuracy. Come 2022, the integration of the GPT-4 model introduces a shift in the search engine sphere, revolutionizing how users engage with digital content and search engines’ algorithmic capabilities.
2023 - Onwards: Quantum Search Engines
Ready for a cheat tour of the future of search engines? Here it is – Quantum computing. Undoubtedly, quantum search engines will mark the next big shift in digital searching that we’ll come to experience over the next couple of years. Thanks to the advanced processing power of quantum computers that are rumored to enhance search engine efficiency and accuracy at an astonishing pace while significantly minimizing energy consumption. This quantum shift is something the digital escape awaits with anticipation. Till then, let’s pop the corns and enjoy the suspense!
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the history of search engines has been a fascinating journey, punctuated by significant innovations, trend-defining landmarks, and fierce competition. They’ve undergone a dramatic evolution, continually adapting, learning, and advancing with the times, digitizing our quest for knowledge at a pace unimagined until only a few short decades ago.
Each step has reflected a remarkable technological feat, propelling us miles forward into the panorama of digital exploration. Our search engines have evolved from simplicity to complexity, from impersonal to private – catering to every curveball the digital revolution threw at us and upgrading the way we process information on the web.
Frequently Asked questions
The first-ever search engine was The Wanderer, invented by Mark McCahill and his project group. However, this command-line search engine only became available to the broader network of schools joined by a national network. The first web-based search engine introduced to the public was Archie, which came to life in 1992.
Google was invented by two Stanford Ph.D. students Larry Page and Sergey Brin. They developed and launched Google in 1997, initially only accessing Stanford University’s network before making it publicly available in 1998.
From the moment the World Wide Web was cultivated, it was clear that some form of direction would be required for users to navigate the vast information landscape. That’s where search engines came in – they made interfacing with the digital expanse more convenient and comprehensible, leading user’s inquiries to the proper URLs.
Beyond Google, there is a wide array of search engines available on the web today with various features and appeals. Bing is Microsoft’s search engine. Yahoo Search, while being powered by Bing, maintains its separate entity. Then there are other alternative search engines like DuckDuckGo, which maintains user privacy, Yandex, Russia’s leading search engine and Baidu, China’s top search engine.